The results of this collaboration are published in the prestigious journal IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering (according to the Scopus database, this journal ranks 1st out of 118 in the field of Medicine Rehabilitation) in an article entitled Numerical Analysis of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Application in Patients with Orofacial Pain.
Entire paper can be found at https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9727114.
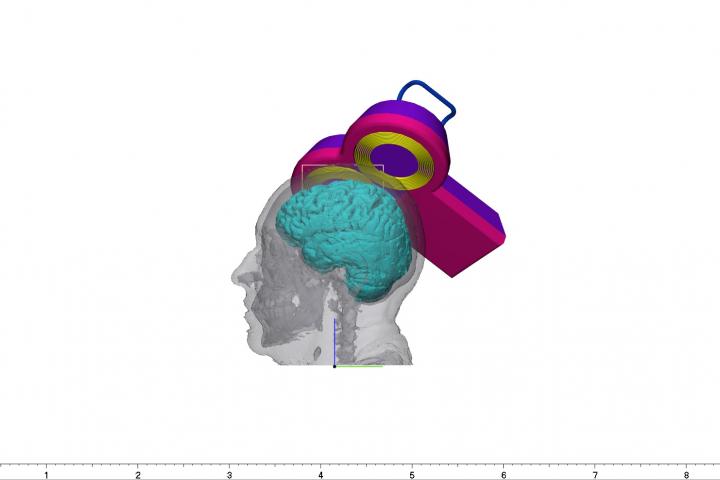
Doc. David Vrba from FBMI explains: "The aim of the study was to verify the appropriate position and orientation of the stimulation coil and the setting of the stimulation protocol using numerical calculations. Based on the segmentation, it was possible to create a detailed 3D model of each patient's head from the MRI images. Using functional MRI, the region in the gray cortex responsible for orofacial pain perception was identified in each patient. The accuracy of the therapy was then evaluated using the distribution of electric field strength in the area of orofacial pain perception."
From the published results, which were correlated with the results of the therapy, it is clear that with proper targeting the device is able to sufficiently stimulate the orofacial pain area. In this type of therapy, the correct placement of the stimulation coil and the adjustment of the amplitude of the excitation current pulse are crucial. The study provides comprehensive information on the influence of these parameters, which can help physicians operating stimulation devices to improve the treatment effectivity.
The Bio-electromagnetism team at FBMI specializes in numerical modeling of electromagnetic field interaction with biological tissues and relevant medical applications. Numerical modelling can be used, for example, for treatment planning, where it is possible to determine the optimal parameters of the treatment in advance to ensure its maximum effectiveness. This procedure can also be performed retrospectively to verify the correct setting of the therapy. A current trend in this area is the use of anatomically accurate patient models in combination with specific therapeutic or diagnostic devices. The Bio-electromagnetism team is mainly involved in radiofrequency and microwave applications such as RF ablation, microwave hyperthermia and microwave imaging, as well as electrical and magnetic stimulation and electroporation.
